Socioeconomic Diversity of Economics PhDs—Robert Schultz and Anna Stansbury →
The parents of economics PhDs have higher levels of education than do those with PhDs in other disciplines.
A Partisan Nonpartisan Blog: Cutting Through Confusion Since 2012
The parents of economics PhDs have higher levels of education than do those with PhDs in other disciplines.
Flying blind is a bad idea. Indeed, if you can help it, trying to manage life without the full benefit of any of your 11 senses is a bad idea. Why I am I talking about 11 senses, when most of us were only taught about 5 in kindergarten? Sanjay Gupta explains in Keep Sharp: Build a Better Brain at Any Age:
You can likely name all five senses: sight (ophthalmoception), smell (olfacoception), taste (gustaoception), touch (tactioception), and hearing (audioception). But there are others with the “cept” ending, which is Latin for take or receive. The other six senses are also processed in the brain and give us more data about the outside world:
Proprioception: A sense of where your body parts are and what they’re doing.
Equilibrioception: A sense of balance, otherwise known as your internal GPS. This tells you if you’re sitting, standing, or lying down. It’s located in the inner ear (which is why problems in your inner ear can cause vertigo).
Nociception: A sense of pain.
Thermo(re)ception: A sense of temperature.
Chronoception: A sense of the passage of time.
Interoception: A sense of your internal needs, like hunger, thirst, needing to use the bathroom.
In addition, I have heard that in Buddhist tradition, the awareness of what is in one’s own mind is counted as a sense. The emotional side of that is not entirely separate from the internal senses in Sanjay Gupta’s list, since people are often aware of their emotions through noticing associated bodily sensations. Closely noticing those bodily sensations is not only a way to be more sensitive to your own emotions, but is also a way to distance yourself enough from the driving force of your emotions to make those emotions easier to manage and deal with skillfully: getting the information and oomph from your emotions without being controlled by them.
On the more physical side, being aware of your own internal state is valuable for many reasons. Most obviously, noticing your internal state can warn you of problems. Less obviously, noticing your internal state can give you a time series to match up to things such as diet and exercise time series to see what makes you feel good and what makes you feel crummy an hour or so after eating or exercising.
At a more philosophical level, to the extent you can stand to notice what is going on in all of your senses, and do so, the more complete the range of your experience as a human being. There is a beauty in that.
For annotated links to other posts on diet and health, see:
My friend and University of Michigan colleague Josh Hausman has a piece in the Atlantic on Covid-generated inflation.
I am a Unitarian-Universalist lay preacher. I gave 12 sermons—annually from 2005 to 2016—to the Community Unitarian Universalists in Brighton. (In 2016 I moved to Colorado.) This post was the first of those, which in turn reprised the same account of what I believed at that point that I spoke in Fall 2000 to the First Unitarian Universalist Congregation of Ann Arbor. (Actually, it was “Church” rather than “Congregation” back then.) That talk in Fall 2000 came after I had taken Ken Phifer’s course “Building Your Own Theology” and three weeks after I officially joined the First Unitarian Universality Congregation of Ann Arbor by “signing the book.” I date my change in self-identification as a Mormon to self-identification as a Unitarian-Universalist to that moment. What you see below is very lightly edited from what I said in Fall 2000.
This now completes on my blog the full set of 12 Unitarian Universalist sermons that I have given. Here are the links in chronological order of when I gave each sermon:
Sharing Epiphanies (including the video)
The Message of Mormonism for Atheists Who Want to Stay Atheists (video here)
I also have three of Ken Phifer’s sermons on my blog:
At the bottom of this post are links to some of my other posts on religion.
Hi, my name is Miles Kimball. I wish you could have heard all of the credos that I heard in the latest Building Your Own Theology course, but I may be the only one foolhardy enough to get up here at the pulpit to give mine. In any case, my credo is not in any way representative of the wonderful variety of different things people had to say. But here it is.
I grew up in the Mormon Church. All of my ancestors for many generations have belonged to the Mormon Church and my grandfather was the President of the entire Mormon Church until he died in 1985. So why am I a Unitarian-Universalist now?
When I was young, Mormonism seemed true to me just like science is true and I reveled in the intellectual playground of Mormon doctrine. In addition to some standard Christian doctrines about Jesus, Mormonism has a set of doctrines that sound a lot like modern science fiction, despite being developed in the first half of the 19th century. It is no accident that Utah is now a kind of Mecca for science fiction writers. It is a common speculation among Mormons that God the Father is only one of a long line of gods, each of whom went off to create a new planet, had billions of literal spirit children and sent those spirit children down into physical bodies to gain experience and prove their worthiness to themselves become gods. What is official doctrine is that we can go on to become gods who create new worlds if we are totally faithful and valiant in adhering to the tenets of Mormonism.
When I went off to college at Harvard, I vigorously defended Mormonism to my curious classmates. I soon realized that in the East, Mormonism to my classmates was whatever I told them it was. So in defending my religion, I started bit by bit to smooth off the sharp edges and modifying things to make Mormonism more consistent with what I knew of science and social justice. One of the most embarrassing things about Mormonism was its refusal to let African Americans be priests, when it made all faithful men of other races priests (including me). Even though my grandfather changed that racist policy in 1978, it still took a lot of explaining to rationalize why it had been there in the first place.
On the side of science, the biggest issue was evolution, but without ever having studied evolution I was able to convince myself that the sequence of fossils in the fossil record would make plenty of sense as the way God would have done things.
When I was 19, I took time off from college and spent two years as a Mormon missionary in Japan and had a positive experience with that, except for the constant pressure to work harder. I saw that Mormonism had a positive effect on the lives of those who chose to join it because they saw something valuable in it for them.
I got married a year after I had started a Ph.D. program in Economics. Encouraged by the Mormon teachings about the importance of children, we immediately dived into childbearing. Of our five children, two died in infancy. The priesthood powers I held that were supposed to allow me, I thought, to heal by the power of God did not work in my case. Those losses drove me to a deeper searching for spiritual truth---or maybe it was psychological truth. I had four arenas to explore my religion in depth. I had many talks with my wife who was on her own religious journey; I talked on a regular basis to a group of Mormon men who had an uncompromising commitment to the truth; I led an adult Sunday School class that become more and more emotionally honest as time went on; and I taught a course on evolution at the University of Michigan, using Daniel Dennett’s hard-hitting book Darwin’s Dangerous Idea as the main text. I worked hard to spell out each new emotional and intellectual insight as a part of Mormonism. At first I felt I could successfully encompass my new insights within Mormonism, using texts from the large array of Mormon scriptures and quasi-scriptures. But I began to get an inkling that the leaders of the Mormon Church did not share my view of the doctrine when they began to excommunicate leading historians, intellectuals and feminists in the Mormon Church and fire others from their jobs at Brigham Young University (BYU). Amazingly, I did not fully believe my ears and eyes about the thinking of the Church leaders until I had occasion to interview for a job at BYU and had a long talk with one of the Church’s apostles, my father’s cousin, who was himself the son of an eminent chemist. One of the main threads I heard in that conversation was the thought-control the apostle used on himself in order to not think too deeply about his own disagreements with his more senior colleagues. Along the way, they effectively made a decision that I was not orthodox enough for a job at BYU, though there was still some hope for my reformation. My growing knowledge of evolution and a greater awareness of the limitations of physics combined with this final loss of faith in the institution of the Mormon Church to erode my belief in miracles and in the afterlife. A year and a half ago, I was disturbed to realize I was no longer a Christian when I started to wonder at what terrible force could have created the necessity for him to suffer and die for our sins.
I wanted to have someplace where I could wrestle with thorny questions about God, Christ, the afterlife etc., without being scolded for raising such issues. I started attending the First Unitarian Universality Church of Ann Arbor at the beginning of 2000. Not long after, my local bishop officially decided that I was unfit to teach or speak in the Mormon Church any more. That made the transition much easier. I feel very lucky to have had my whole family make the same transition, though as part of their own, very different, individual religious journeys. For me, signing the book three weeks ago represented the start of a new life.
I still can’t help the Mormon influences on my thinking about the Universe. I find myself trying to give a theological meaning to the science I read. For example, I wonder if the creative powers of evolution, cosmic inflation and quantum mechanics in its many worlds interpretation can be considered Creator Gods. I ponder the subjective spiritual experiences I read and hear about and that I have had myself and ask myself whether they point to a God within us, even if it that God within can ultimately be explained as the result of the laws of physics. I marvel at the emotional and intellectual depth of groups of human beings sharing the thoughts and feelings of their hearts and think I see the shape of a God arising from free human beings interacting that is as much greater than those individual free human beings as our brains are more intelligent than an individual neuron.
These are now my Gods of the past, present and future.
No one knows the future, but I know the kind of future that I would like to take part in building. I want to stand for all people being joined together in discovery and wonder.
I want to stand for humanity going beyond just solving its problems. I hope to see humanity reach for the stars, not only in the science fiction sense that I have loved so well but in every dimension of the human heart and soul.
Don't miss these posts on Mormonism:
The Message of Mormonism for Atheists Who Want to Stay Atheists
How Conservative Mormon America Avoided the Fate of Conservative White America
The Mormon Church Decides to Treat Gay Marriage as Rebellion on a Par with Polygamy
David Holland on the Mormon Church During the February 3, 2008–January 2, 2018 Monson Administration
Other Posts on Religion:
Posts on Positive Mental Health and Maintaining One’s Moral Compass:
Co-Active Coaching as a Tool for Maximizing Utility—Getting Where You Want in Life
How Economists Can Enhance Their Scientific Creativity, Engagement and Impact
Judson Brewer, Elizabeth Bernstein and Mitchell Kaplan on Finding Inner Calm
Recognizing Opportunity: The Case of the Golden Raspberries—Taryn Laakso
Taryn Laakso: Battery Charge Trending to 0% — Time to Recharge
Savannah Taylor: Lessons of the Labyrinth and Tapping Into Your Inner Wisdom
The International Monetary Fund asked me and my coauthors Dan Benjamin, Kristen Cooper and Ori Heffetz to write about our efforts to work out the principles for a national well-being index that could function as a coequal to GDP in understanding how a nation is doing. Here it is on an IMF website. And with their permission, the full text is below. I also did an associated podcast, which I’ll feature next Thursday, but here is the associated podcast if you want to listen to it now.
The search continues for a better gauge of prosperity than GDP alone
Gross domestic product (GDP), which measures the total output of goods and services in an economy, has flaws when used to gauge the well-being of a nation’s residents.
For example, to the question of whether people in the United States are better-off in 2021 than they were before the COVID-19 pandemic, the answer would be yes, slightly, if per capita GDP is the yardstick. That’s because real (inflation-adjusted) per capita GDP rose from $58,333 in the fourth quarter of 2019 to $58,454 in the second quarter of 2021.
But that affirmative answer is likely to ring hollow to many. The United States does not appear better-off. It experienced a fourth wave of COVID-19 infections in late 2021 that left thousands dead. Many businesses are still shuttered, and millions remain unemployed. The country is deeply divided socially and politically. GDP captures neither the enormous human costs of the pandemic, nor the nation’s social and emotional disruptions.
The recognition that GDP cannot encompass many dimensions of well-being has prompted efforts to develop measures that reflect a more complete account of what people care about. The idea is not to give up on GDP—nor to replace it with some other one-dimensional measure, such as self-reported life satisfaction, which, like GDP, gives only a partial and hence potentially misleading picture. Instead, a measure that captures many dimensions of national well-being and complements GDP is needed. Fleurbaey and Blanchet (2013) provide an overview of this idea as well as many other so-called Beyond GDP proposals and initiatives.
In this article, we discuss the Human Development Index (HDI), an alternate measure of well-being that has been influential in developing economies. We then turn to our proposed approach to measuring national well-being, which is based on aggregating people’s survey responses about many dimensions of their welfare.
The HDI’s roots are in the capabilities approach to well-being advanced by Amartya Sen (1985). Capabilities are the features of individuals and their state of life that determine the activities and internal experiences a person can effectively choose. The approach puts a direct value on freedom in the practical sense of what an individual can do. Martha Nussbaum (2011) elaborated on Sen’s idea by offering a concrete list of core capabilities—including life span, health, freedom from violence and constraint, imagination and thought, emotions, freedom to chart one’s own course in life, good social relationships, the natural world, play, political participation, and property rights.
The HDI transforms several dimensions of well-being into a single yearly index to rate a country’s performance. Sen was leery of aggregating measures of different capabilities. But when policymaking requires trade-offs, judging whether one policy is better than the alternatives requires an index. Moreover, having a single number makes it difficult for government officials to cherry-pick whichever statistic makes things look rosiest. Creating an index requires weighting the capabilities relative to one another.
For GDP, prices provide the weights for the goods and services it includes. But because GDP relies on market transaction data, it fails to include things human beings care about that do not run through the market—such as leisure time, relationships with family and friends, and emotional experiences such as anxiety and sense of purpose. Moreover, although prices may represent the relative importance of different market goods and services to the well-being of an individual or household, they do not countenance the possibility that a dollar spent by a family in poverty might do more for national well-being than one spent by a billionaire’s family.
On its website, the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) describes the HDI as “created to emphasize that people and their capabilities should be the ultimate criteria for assessing the development of a country, not economic growth alone.” But after those lofty words, the description turns to technical detail: “HDI is a summary measure of average achievement in key dimensions of human development: a long and healthy life, being knowledgeable, and having a decent standard of living. The HDI is the geometric mean of normalized indices for each of the three dimensions.”
The technical details determine how the UNDP puts into practice its lofty goal: which dimensions of well-being (or capabilities) the HDI tracks, what it leaves out, and what relative importance it gives to the things it does track. For example, according to the geometric mean used by the HDI, a percentage change in HDI is the equally weighted average of the percentage changes of its components.
The HDI is surely the best-known practical application of Sen’s capabilities approach. It provides a single, simple number that both summarizes the state of a country at a point in time and is easy to construct and explain.
Still, although it captures more dimensions of well-being than GDP does, the HDI is arbitrary in its choice of what to include and how to weight what it does cover. The goal of an enhanced well-being index is to include many more than three dimensions of well-being and to weight them based on the values of the people in the country.
A major reason the HDI focuses on longevity, education, and income is that when the index was introduced in 1990, these important dimensions of a good life were among the few variables being widely measured across countries in a reasonably comparable way. Unavailability of data has similarly constrained the reach of other Beyond GDP initiatives—such as the Genuine Progress Indicator and the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development’s (OECD’s) Better Life Index. But lack of current data should not constrain our vision of what a good index should look like.
Some Beyond GDP initiatives have gotten around these data constraints by using surveys, which can be conducted relatively cheaply around the world in real time. Indeed, real time is crucial to policymaking. For example, how the HDI performed during the pandemic is still unknown because, at the time of this writing, the latest numbers available are for 2019.
Some researchers have proposed using single-question survey measures of happiness or life satisfaction. However, research, including some of our own with Alex Rees-Jones of the University of Pennsylvania, suggests that answers to these survey questions do not capture the full range of what people care about when they make choices. Partly to address this shortcoming, other Beyond GDP initiatives, such as those of the OECD and the UK Office of National Statistics, ask additional survey questions to measure dimensions of well-being other than happiness or life satisfaction. But multiple survey questions reintroduce the question of how to weight the dimensions of well-being relative to one another.
Our research makes clear the importance including multiple components in a measure of national well-being and the importance of getting the weighting right. Those issues are at the core of our efforts to construct a theoretically sound well-being index. The weights we recommend are relative marginal utilities—traditionally defined as the additional satisfaction an individual realizes from one more unit of a good or service, but in this case from one more unit of an aspect of well-being. We propose to estimate marginal utilities based on stated preferences in specially designed surveys, described below.
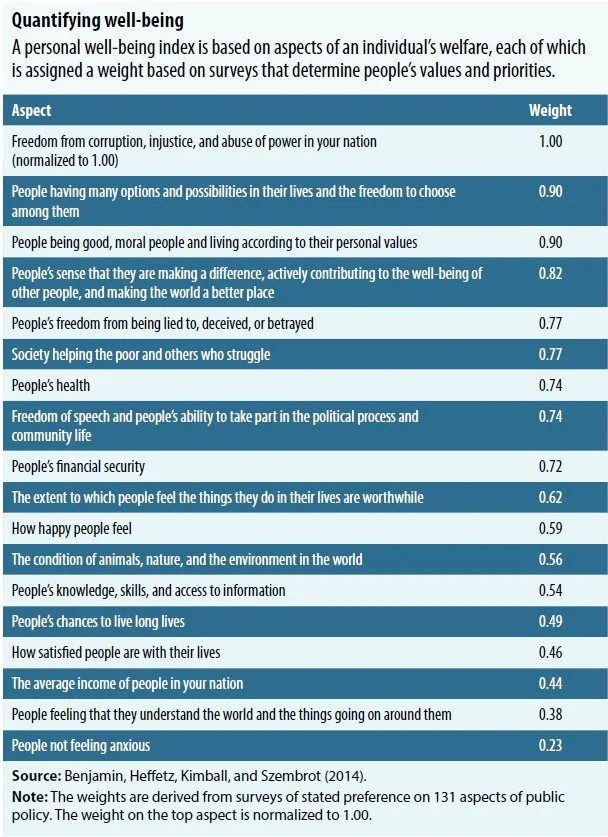
Some older results illustrate our approach, which we are still developing. In Benjamin, Heffetz, Kimball, and Szembrot (2014) we asked survey questions about 136 aspects of well-being—a list that aimed to comprehensively reflect all proposed aspects of well-being. (An actual index should comprise fewer aspects of well-being and avoid, or adjust for, conceptual overlaps.) The table shows estimated weights based on policy choices—described as “national policy questions that you and everyone else in your nation vote on.” Respondents chose between pairs of hypothetical policies, which involved trade-offs between aspects of well-being. Our statistical procedure inferred weights for the aspects of well-being based on respondents’ choices, so that an aspect of well-being is assigned higher weight if it has a bigger impact on the policy respondents preferred. Because of space constraints, the table illustrates the results using 18 of the 136 aspects of well-being: the three with the highest weights, other interesting aspects in the top 10, every aspect that seems closely related to HDI components, other aspects for which data are widely collected, and an aspect on the natural environment. We normalize the weight on the top aspect—freedom from corruption, injustice, and abuse of power—to 1.00.
Although many things could be said about the table, we limit ourselves to three points.
Many of the top aspects are clearly capabilities in Sen’s sense, including the first one, which does not guarantee a good life, but helps make one possible.
A number of important aspects of well-being—with weights of at least 75 percent of the top aspect—are missing from many measures of national well-being, such as the HDI.
The weights for many aspects of well-being that have received much attention are well below the weights for those at the top. For example, “people not feeling anxious”—one of four aspects collected in large samples of individuals by the UK Office of National Statistics—is weighted less than a quarter of the top aspect. For those relevant to the HDI, “people’s health” and “people’s financial security” have almost three-quarters the weight of the top aspect, but others—knowledge, skills, and access to information; understanding the world; long lives; and average income—have weights no higher than 54 percent of the top aspect.
To construct personal well-being indices—which are aggregated to develop a national well-being index—our approach involves asking two types of survey questions about the aspects of well-being: ratings and trade-offs. In a rating question, respondents move a slider from 0 to 100 to indicate their level of an aspect of well-being over the past year. In a trade-off question, respondents choose between two options. In each trade-off option, the level of one or more aspects of well-being is slightly higher or slightly lower than the reported level in the rating question. In the illustration above, the choices between national policies are examples of trade-off questions.
In Benjamin, Heffetz, Kimball, and Szembrot (2014) we argue that for an individual, a well-being index can be constructed similarly to the way consumption is measured in the national accounts that are used in calculating GDP. Consumption calculations rely on quantities and prices. To compute a well-being index, reported levels of aspects of well-being from the rating questions are substituted for quantities, while the weights reported in the table are used in place of prices. The weights—derived from the trade-off questions that reveal the choices people make between aspects of well-being—represent people’s values and priorities.
In Benjamin, Cooper, Heffetz, and Kimball (2017) we lay out how much remains to be done to develop a full national well-being index that is consistent with modern welfare theory in economics. Here are three areas in which we have made the most progress to date.
First, large differences in how different people use any given scale for measuring their well-being make well-being measures seem subjective. We developed what we call “calibration questions” to test for systematic differences in people’s scale use—for example, some people use the whole scale, from 0 to 100, and others use only 50 to 100. We can use calibration ratings to correct for some such scale-use differences—both across individuals and even potentially across time for the same individual.
Second, we hypothesize that the trade-offs people make between different aspects of well-being are likely to differ according to demographics—such as age and education—and how well-off people are overall. We can use such systematic tendencies to create reasonable weights without needing a huge amount of data to estimate each individual’s weights.
Third, we propose that the index take into account inequality—not just in income or wealth, but in personal well-being. We do not assume that an index of personal well-being can be simply added up across people to get a national index. That would imply, for example, that national well-being is at the same level whether everyone is at 50 or half the people are at 10 and half are at 90. If as a society we judge the more equal situation to be better, that society has some degree of aversion to well-being inequality, which requires employing a level of inequality aversion to transform the personal well-being indices before totaling them to obtain a national index.
“What gets measured, gets treasured” is an important maxim. In the well-being sphere, this means policymakers and development practitioners should carefully consider which metrics they monitor. Perhaps equally important, though, is properly weighting them. We can add a new adage: “What we give weight to, we value.”
References:
Benjamin, Daniel J., Kristen B. Cooper, Ori Heffetz, and Miles S. Kimball. 2017. “Challenges in Constructing a Survey-Based Well-Being Index.” American Economic Review 107 (5): 81–85.
Benjamin, Daniel J., Ori Heffetz, Miles S. Kimball, and Nichole Szembrot. 2014. “Beyond Happiness and Satisfaction: Toward Well-Being Indices Based on Stated Preference.” American Economic Review 104 (9): 2698–735.
Fleurbaey, Marc, and Didier Blanchet. 2013. Beyond GDP: Measuring Welfare and Assessing Sustainability. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press.
Nussbaum, Martha. 2011. Creating Capabilities: The Human Development Approach. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Sen, Amartya. 1985. Commodities and Capabilities. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press.
Opinions expressed in articles and other materials are those of the authors; they do not necessarily represent the views of the IMF and its Executive Board, or IMF policy.
Don’t miss these other posts related to happiness and well-being
What if a big part of the benefit of aerobic exercise is that it strengthens one’s diaphragm? (Abundant oxygenation may be important.) If so, then an exercise that directly focused on strengthening one’s diaphragm might be quite beneficial. The device shown above provides resistance for breathing—the moral equivalent of weights for one’s diaphragm. Evidence shows that inspiratory strength training is, indeed, quite beneficial. See this post:
I was ready to take this research seriously because of other things I had read about the quality of one’s breathing as a key factor for health. See these posts:
When I asked my doctor about inspiratory strength training, he said “Just go to a medical supply store.” It turns out Amazon is a great medical supply store. There are many options that might be equally good or even somewhat better, but the device I actually bought for breath resistance training was the “Breather” shown above. (There are some videos online they direct you to for instructions on the exercises.) I haven’t been using it for long at all, but I already feel that I am breathing easier from the little bit of breath strength training I have done. I am betting that, per minute spent, this is a very effective exercise for improving health.
I plan to keep doing these breathing exercises. If one of you tries this out, let me know your take on them.
P.S. I should say that the very first “Breather” I got had a dial that was stuck and wouldn’t turn. I just bought another one, which doesn’t have that problem. I was in a forgiving mood because the benefits of the breathing exercises themselves are so good.
For annotated links to other posts on diet and health, see:
The 13th, 14th and 15th amendments to the US Constitution transformed the Constitution by (ultimately) coming close to making the states subject to the Bill of Rights, as well as specifically declaring that states could not treat certain races as second-class citizens (a prohibition on the states that was not enforced for a long time). But there were some key limitations on state power in the original text of the US Constitution even before any amendments. Most obviously, the supremacy clause made null and void in court any state attempt to contravene a legitimate federal exercise of power:
This Constitution and the laws of the United States which shall be made in pursuance thereof, and all treaties made, or which shall be made, under the authority of the United States, shall be the supreme law of the land, and the judges in every State shall be bound thereby, any thing in the constitution or laws of any State to the contrary notwithstanding.
As a key support structure for the supremacy of the Constitution, state officials are required to swear allegiance and obedience to it:
The Senators and Representatives, and the members of the several State legislatures, and all executive and judicial officers, both of the United States and the several States, shall be bound by oath or affirmation to support this Constitution.
And there is a reminder that the enumerated powers in the Constitution are for real by the declaration that they are accompanied by everything logically necessary to their performance:
… power to make all laws which shall be necessary and proper for carrying into execution the foregoing powers, and all other powers vested by this Constitution in the government of the United States, or in any department or officer thereof.
States were also required to adhere to some basic republican principles—the rule of law, the sanctity of contract and social equality:
No State shall … pass any bill of attainder, ex-post-facto law, or law impairing the obligation of contracts; or grant any title of nobility
The Constitution gave the federal government a monopoly over foreign policy, over conduct of war (except in exigent situations) and over monetary policy:
No State shall enter into any treaty, alliance, or confederation; grant letters of marque and reprisal; coin money; emit bills of credit; make any thing but gold and silver a legal tender in payment of debts …
And the Constitution gave the federal government a monopoly over trade policy:
No State shall, without the consent of the Congress, lay any imposts or duties on imports or exports, except what may be absolutely necessary for executing its inspection laws, and the net produce of all duties and imposts laid by any State on imports or exports, shall be for the use of the treasury of the United States; and all such laws shall be subject to the revision and control of the Congress. No State shall, without the consent of Congress, lay any duty on tonnage, keep troops or ships of war in time of peace, enter into any agreement or compact with another State, or with a foreign power, or engage in war unless actually invaded, or in such imminent danger as will not admit of delay.
The requirement that the states adhere to basic republican principles and give the federal government a monopoly over foreign policy, conduct of war, monetary policy and trade policy were not controversial. What was controversial was a transition from what was in many cases only a theoretical power of the national government to a genuine power of the national government under the Constitutions supremacy and “necessary and proper” clauses and the required oaths by state officials to uphold the Constitution.
In the Federalist Papers #44, James Madison argues that these controversial clauses giving genuine as opposed to fictive power to the national government was absolutely necessary. He writes in the Federalist Papers #44:
The question, therefore, whether this amount of power shall be granted or not, resolves itself into another question, whether or not a government commensurate to the exigencies of the Union shall be established; or, in other words, whether the Union itself shall be preserved.
James Madison also references several previous numbers in saying:
We have now reviewed, in detail, all the articles composing the sum or quantity of power delegated by the proposed Constitution to the federal government, and are brought to this undeniable conclusion, that no part of the power is unnecessary or improper for accomplishing the necessary objects of the Union.
The full text of the Federalist Papers #44 is immediately below. And below that is a set of links to posts on all the earlier Federalist Papers, including those of his own that James Madison was referring to.
FEDERALIST NO. 44
Restrictions on the Authority of the Several States
From the New York Packet
Friday, January 25, 1788.
Author: James Madison
To the People of the State of New York:
A FIFTH class of provisions in favor of the federal authority consists of the following restrictions on the authority of the several States:1. "No State shall enter into any treaty, alliance, or confederation; grant letters of marque and reprisal; coin money; emit bills of credit; make any thing but gold and silver a legal tender in payment of debts; pass any bill of attainder, ex-post-facto law, or law impairing the obligation of contracts; or grant any title of nobility. "The prohibition against treaties, alliances, and confederations makes a part of the existing articles of Union; and for reasons which need no explanation, is copied into the new Constitution. The prohibition of letters of marque is another part of the old system, but is somewhat extended in the new. According to the former, letters of marque could be granted by the States after a declaration of war; according to the latter, these licenses must be obtained, as well during war as previous to its declaration, from the government of the United States. This alteration is fully justified by the advantage of uniformity in all points which relate to foreign powers; and of immediate responsibility to the nation in all those for whose conduct the nation itself is to be responsible.
The right of coining money, which is here taken from the States, was left in their hands by the Confederation, as a concurrent right with that of Congress, under an exception in favor of the exclusive right of Congress to regulate the alloy and value. In this instance, also, the new provision is an improvement on the old. Whilst the alloy and value depended on the general authority, a right of coinage in the particular States could have no other effect than to multiply expensive mints and diversify the forms and weights of the circulating pieces. The latter inconveniency defeats one purpose for which the power was originally submitted to the federal head; and as far as the former might prevent an inconvenient remittance of gold and silver to the central mint for recoinage, the end can be as well attained by local mints established under the general authority.
The extension of the prohibition to bills of credit must give pleasure to every citizen, in proportion to his love of justice and his knowledge of the true springs of public prosperity. The loss which America has sustained since the peace, from the pestilent effects of paper money on the necessary confidence between man and man, on the necessary confidence in the public councils, on the industry and morals of the people, and on the character of republican government, constitutes an enormous debt against the States chargeable with this unadvised measure, which must long remain unsatisfied; or rather an accumulation of guilt, which can be expiated no otherwise than by a voluntary sacrifice on the altar of justice, of the power which has been the instrument of it. In addition to these persuasive considerations, it may be observed, that the same reasons which show the necessity of denying to the States the power of regulating coin, prove with equal force that they ought not to be at liberty to substitute a paper medium in the place of coin. Had every State a right to regulate the value of its coin, there might be as many different currencies as States, and thus the intercourse among them would be impeded; retrospective alterations in its value might be made, and thus the citizens of other States be injured, and animosities be kindled among the States themselves. The subjects of foreign powers might suffer from the same cause, and hence the Union be discredited and embroiled by the indiscretion of a single member. No one of these mischiefs is less incident to a power in the States to emit paper money, than to coin gold or silver. The power to make any thing but gold and silver a tender in payment of debts, is withdrawn from the States, on the same principle with that of issuing a paper currency. Bills of attainder, ex-post-facto laws, and laws impairing the obligation of contracts, are contrary to the first principles of the social compact, and to every principle of sound legislation. The two former are expressly prohibited by the declarations prefixed to some of the State constitutions, and all of them are prohibited by the spirit and scope of these fundamental charters. Our own experience has taught us, nevertheless, that additional fences against these dangers ought not to be omitted. Very properly, therefore, have the convention added this constitutional bulwark in favor of personal security and private rights; and I am much deceived if they have not, in so doing, as faithfully consulted the genuine sentiments as the undoubted interests of their constituents. The sober people of America are weary of the fluctuating policy which has directed the public councils. They have seen with regret and indignation that sudden changes and legislative interferences, in cases affecting personal rights, become jobs in the hands of enterprising and influential speculators, and snares to the more-industrious and lessinformed part of the community. They have seen, too, that one legislative interference is but the first link of a long chain of repetitions, every subsequent interference being naturally produced by the effects of the preceding. They very rightly infer, therefore, that some thorough reform is wanting, which will banish speculations on public measures, inspire a general prudence and industry, and give a regular course to the business of society. The prohibition with respect to titles of nobility is copied from the articles of Confederation and needs no comment. 2. "No State shall, without the consent of the Congress, lay any imposts or duties on imports or exports, except what may be absolutely necessary for executing its inspection laws, and the net produce of all duties and imposts laid by any State on imports or exports, shall be for the use of the treasury of the United States; and all such laws shall be subject to the revision and control of the Congress. No State shall, without the consent of Congress, lay any duty on tonnage, keep troops or ships of war in time of peace, enter into any agreement or compact with another State, or with a foreign power, or engage in war unless actually invaded, or in such imminent danger as will not admit of delay. "The restraint on the power of the States over imports and exports is enforced by all the arguments which prove the necessity of submitting the regulation of trade to the federal councils. It is needless, therefore, to remark further on this head, than that the manner in which the restraint is qualified seems well calculated at once to secure to the States a reasonable discretion in providing for the conveniency of their imports and exports, and to the United States a reasonable check against the abuse of this discretion.
The remaining particulars of this clause fall within reasonings which are either so obvious, or have been so fully developed, that they may be passed over without remark. The SIXTH and last class consists of the several powers and provisions by which efficacy is given to all the rest. 1. Of these the first is, the "power to make all laws which shall be necessary and proper for carrying into execution the foregoing powers, and all other powers vested by this Constitution in the government of the United States, or in any department or officer thereof. "Few parts of the Constitution have been assailed with more intemperance than this; yet on a fair investigation of it, no part can appear more completely invulnerable. Without the SUBSTANCE of this power, the whole Constitution would be a dead letter. Those who object to the article, therefore, as a part of the Constitution, can only mean that the FORM of the provision is improper. But have they considered whether a better form could have been substituted? There are four other possible methods which the Constitution might have taken on this subject. They might have copied the second article of the existing Confederation, which would have prohibited the exercise of any power not EXPRESSLY delegated; they might have attempted a positive enumeration of the powers comprehended under the general terms "necessary and proper"; they might have attempted a negative enumeration of them, by specifying the powers excepted from the general definition; they might have been altogether silent on the subject, leaving these necessary and proper powers to construction and inference. Had the convention taken the first method of adopting the second article of Confederation, it is evident that the new Congress would be continually exposed, as their predecessors have been, to the alternative of construing the term "EXPRESSLY" with so much rigor, as to disarm the government of all real authority whatever, or with so much latitude as to destroy altogether the force of the restriction.
It would be easy to show, if it were necessary, that no important power, delegated by the articles of Confederation, has been or can be executed by Congress, without recurring more or less to the doctrine of CONSTRUCTION or IMPLICATION. As the powers delegated under the new system are more extensive, the government which is to administer it would find itself still more distressed with the alternative of betraying the public interests by doing nothing, or of violating the Constitution by exercising powers indispensably necessary and proper, but, at the same time, not EXPRESSLY granted. Had the convention attempted a positive enumeration of the powers necessary and proper for carrying their other powers into effect, the attempt would have involved a complete digest of laws on every subject to which the Constitution relates; accommodated too, not only to the existing state of things, but to all the possible changes which futurity may produce; for in every new application of a general power, the PARTICULAR POWERS, which are the means of attaining the OBJECT of the general power, must always necessarily vary with that object, and be often properly varied whilst the object remains the same.
Had they attempted to enumerate the particular powers or means not necessary or proper for carrying the general powers into execution, the task would have been no less chimerical; and would have been liable to this further objection, that every defect in the enumeration would have been equivalent to a positive grant of authority. If, to avoid this consequence, they had attempted a partial enumeration of the exceptions, and described the residue by the general terms, NOT NECESSARY OR PROPER, it must have happened that the enumeration would comprehend a few of the excepted powers only; that these would be such as would be least likely to be assumed or tolerated, because the enumeration would of course select such as would be least necessary or proper; and that the unnecessary and improper powers included in the residuum, would be less forcibly excepted, than if no partial enumeration had been made. Had the Constitution been silent on this head, there can be no doubt that all the particular powers requisite as means of executing the general powers would have resulted to the government, by unavoidable implication. No axiom is more clearly established in law, or in reason, than that wherever the end is required, the means are authorized; wherever a general power to do a thing is given, every particular power necessary for doing it is included. Had this last method, therefore, been pursued by the convention, every objection now urged against their plan would remain in all its plausibility; and the real inconveniency would be incurred of not removing a pretext which may be seized on critical occasions for drawing into question the essential powers of the Union. If it be asked what is to be the consequence, in case the Congress shall misconstrue this part of the Constitution, and exercise powers not warranted by its true meaning, I answer, the same as if they should misconstrue or enlarge any other power vested in them; as if the general power had been reduced to particulars, and any one of these were to be violated; the same, in short, as if the State legislatures should violate the irrespective constitutional authorities. In the first instance, the success of the usurpation will depend on the executive and judiciary departments, which are to expound and give effect to the legislative acts; and in the last resort a remedy must be obtained from the people who can, by the election of more faithful representatives, annul the acts of the usurpers. The truth is, that this ultimate redress may be more confided in against unconstitutional acts of the federal than of the State legislatures, for this plain reason, that as every such act of the former will be an invasion of the rights of the latter, these will be ever ready to mark the innovation, to sound the alarm to the people, and to exert their local influence in effecting a change of federal representatives. There being no such intermediate body between the State legislatures and the people interested in watching the conduct of the former, violations of the State constitutions are more likely to remain unnoticed and unredressed. 2. "This Constitution and the laws of the United States which shall be made in pursuance thereof, and all treaties made, or which shall be made, under the authority of the United States, shall be the supreme law of the land, and the judges in every State shall be bound thereby, any thing in the constitution or laws of any State to the contrary notwithstanding. "The indiscreet zeal of the adversaries to the Constitution has betrayed them into an attack on this part of it also, without which it would have been evidently and radically defective. To be fully sensible of this, we need only suppose for a moment that the supremacy of the State constitutions had been left complete by a saving clause in their favor. In the first place, as these constitutions invest the State legislatures with absolute sovereignty, in all cases not excepted by the existing articles of Confederation, all the authorities contained in the proposed Constitution, so far as they exceed those enumerated in the Confederation, would have been annulled, and the new Congress would have been reduced to the same impotent condition with their predecessors. In the next place, as the constitutions of some of the States do not even expressly and fully recognize the existing powers of the Confederacy, an express saving of the supremacy of the former would, in such States, have brought into question every power contained in the proposed Constitution. In the third place, as the constitutions of the States differ much from each other, it might happen that a treaty or national law, of great and equal importance to the States, would interfere with some and not with other constitutions, and would consequently be valid in some of the States, at the same time that it would have no effect in others. In fine, the world would have seen, for the first time, a system of government founded on an inversion of the fundamental principles of all government; it would have seen the authority of the whole society every where subordinate to the authority of the parts; it would have seen a monster, in which the head was under the direction of the members. 3. "The Senators and Representatives, and the members of the several State legislatures, and all executive and judicial officers, both of the United States and the several States, shall be bound by oath or affirmation to support this Constitution. "It has been asked why it was thought necessary, that the State magistracy should be bound to support the federal Constitution, and unnecessary that a like oath should be imposed on the officers of the United States, in favor of the State constitutions. Several reasons might be assigned for the distinction. I content myself with one, which is obvious and conclusive. The members of the federal government will have no agency in carrying the State constitutions into effect. The members and officers of the State governments, on the contrary, will have an essential agency in giving effect to the federal Constitution. The election of the President and Senate will depend, in all cases, on the legislatures of the several States. And the election of the House of Representatives will equally depend on the same authority in the first instance; and will, probably, forever be conducted by the officers, and according to the laws, of the States. 4. Among the provisions for giving efficacy to the federal powers might be added those which belong to the executive and judiciary departments: but as these are reserved for particular examination in another place, I pass them over in this. We have now reviewed, in detail, all the articles composing the sum or quantity of power delegated by the proposed Constitution to the federal government, and are brought to this undeniable conclusion, that no part of the power is unnecessary or improper for accomplishing the necessary objects of the Union. The question, therefore, whether this amount of power shall be granted or not, resolves itself into another question, whether or not a government commensurate to the exigencies of the Union shall be established; or, in other words, whether the Union itself shall be preserved.
PUBLIUS.
Links to my other posts on The Federalist Papers so far:
The Federalist Papers #1: Alexander Hamilton's Plea for Reasoned Debate
The Federalist Papers #3: United, the 13 States are Less Likely to Stumble into War
The Federalist Papers #4 B: National Defense Will Be Stronger if the States are United
The Federalist Papers #5: Unless United, the States Will Be at Each Others' Throats
The Federalist Papers #6 A: Alexander Hamilton on the Many Human Motives for War
The Federalist Papers #11 A: United, the States Can Get a Better Trade Deal—Alexander Hamilton
The Federalist Papers #12: Union Makes it Much Easier to Get Tariff Revenue—Alexander Hamilton
The Federalist Papers #13: Alexander Hamilton on Increasing Returns to Scale in National Government
The Federalist Papers #14: A Republic Can Be Geographically Large—James Madison
The Federalist Papers #21 A: Constitutions Need to be Enforced—Alexander Hamilton
The Federalist Papers #24: The United States Need a Standing Army—Alexander Hamilton
The Federalist Papers #27: People Will Get Used to the Federal Government—Alexander Hamilton
The Federalist Papers #30: A Robust Power of Taxation is Needed to Make a Nation Powerful
The Federalist Papers #35 A: Alexander Hamilton as an Economist
The Federalist Papers #35 B: Alexander Hamilton on Who Can Represent Whom
The Federalist Papers #36: Alexander Hamilton on Regressive Taxation
The Federalist Papers #39: James Madison Downplays How Radical the Proposed Constitution Is
The Federalist Papers #41: James Madison on Tradeoffs—You Can't Have Everything You Want
The Federalist Papers #42: Every Power of the Federal Government Must Be Justified—James Madison
The resources listed at the bottom of the article are for the University of Colorado Boulder, but similar resources exist elsewhere.
I have a simple theory of what it takes to get your paper published in a top economics journal and an analogous theory of what it takes to get hired as an academic economist or in another job where hiring is done on the basis of collective decisions.
For getting published in a top journal, my model is as follows. First, you need to have genuine value added over the previous literature that is easy to articulate. But once the editors and referees can check that box, they feel permission to like the paper for any reason—even a reason they can’t articulate very well.
One of the big implications of this is that how well written the paper is can matter a lot. And as long as you have some definite value added, you can also get points for explaining results that were already in the literature better than the literature does. Editors and referees want to come away from a paper feeling they learned something they didn’t know—or didn’t understand—that they are glad to know.
My model for getting hired by an economics department (or by any other group of economists who make a hiring decision collectively and without too much interference from non-economists) is similar. You might get to the interview stage by checking some boxes, but it is rare to get from the interview stage to a flyout and then an offer without someone advocating for you strongly. If everyone is positive but lukewarm, it probably isn’t going to happen, unless they are really desperate for someone in your field or your category.
What that means is that you have to really impress someone. That means in turn that you have to be interesting, even if being interesting doesn’t seem one hundred percent safe. For those earlier on in graduate school, it means that you should strive to develop your own individuality as an economist (and particularly as a researcher) so that you don’t look like everyone else. Always remember that your success on the market is the maximum over the distilled opinions of all the departments that have a relevant position. It’s OK if some places hate you. You just need one place (or ideally two) to love you. And having a department love you typically depends on first on having at least one economist in that department advocate for you strongly.
If what I have written here gives you a bit different picture of the best strategy for getting hired and published than the picture you had before, I have succeeded in this post. And if you knew all this already, more power to you! Finally, if anyone wants to dispute these models of publication and hiring decisions, I’d be interested to hear about your views.
Seriously failing memory is something we fear in old age. On the other side, an especially good memory can be a great advantage for an academic or in many other jobs. Sanjay Gupta, in his book Keep Sharp: Build a Better Brain at Any Age, gives a basic rundown on memory. There are 3 steps to memory: encoding, storing what should be stored and forgetting other things, and retrieval.
Donald Hebb said “Neurons that fire together wire together.” This is the physiological fact behind learning. Sanjay Gupta puts it this way:
The attachments between brain cells are incredibly dynamic in nature. In other words, they are not fixed like a line of cable. They change and grow (or shrink) continually. Working together in a network, brain cells organize themselves into specialized groups to serve in different kinds of information processing. When one brain cell sends signals to another, the synapse between the two strengthens. The more often a particular signal is sent between them, the stronger the connection grows. That is why “practice makes perfect.” Every time you experience something new, your brain slightly rewires to accommodate that new experience. Novel experiences and learning cause new dendrites to form, whereas repeated behavior and learning cause existing dendrites to become more entrenched. Both are important, of course. The creation of new dendrites, even weak ones, is called plasticity.
Encoding. It wouldn’t make sense for us to remember everything. The first hurdle for an idea or information to get remembered is to be something you pay attention to when you are first exposed to that idea or information. Sanjay:
There is a caveat, however, to all this memory making. You have to pay attention to properly encode a memory…. Because you cannot pay attention to everything you encounter, a lot of potential stimuli is automatically filtered out.
That is why it is so hard for me (and many other people) to learn names: the moment of first meeting someone is packed with other new information beyond the name figure that new person out that competes with their name for attention.
Storing what should be stored and forgetting other things. For academic pursuits, it is especially helpful to know how to get ideas and information from short-term memory into long-term memory. This is necessary because short-term memory can only remember a few things and trying to add more to short-term memory crowds out what was there before. I have a Quartz column about how to get things into long-term memory:
Sanjay Gupta makes the point that forgetting unimportant things is important to making our memory work well:
I should point out that forgetting does have significant value. As I mentioned, if you remembered everything that comes into your brain, your brain would not work properly and your ability to creatively think and imagine would be diminished. Everyday life would be difficult; sure, you’d be able to recall long lists and cite elegiac love poems, but you’d struggle to grasp abstract concepts and even to recognize faces. There’s a group of neurons that are charged with helping the brain to forget, and that are most active at night during sleep when the brain is reorganizing itself and preparing for the next day of incoming information. Scientists discovered these “forgetting” neurons in 2019, which helps us further understand the importance of sleep—and the merits of forgetting. It’s a beautiful paradox: In order to remember, we have to forget to some degree.
The fact that the brain is designed to forget unimportant things is why it is so hard to get academic ideas and information into long-term memory: there often aren’t enough cues to the brain that academic ideas and information are important to you. That is why it takes the kinds of special effort I write about in “The Most Effective Memory Methods are Difficult—and That's Why They Work.”
In addition to need special effort to clue your brain into the value of putting something into long-term memory, two things of great importance on college campuses and many other places can interfere with getting things into long-term memory: alcohol and sleep deprivation. Sanjay writes:
Certain things can interrupt the process of moving a memory from short term to long term, however. Alcohol, for example, puts a glitch in the process. For someone who is intoxicated, the encoding into long-term memory often does not occur very well, or at all…. Sleep deprivation can also disrupt the movement of memories from short to long term. During sleep, your body consolidates and transfers your short-term memories to long-term memories—the kind you’ll have for much of the rest of your life.
Retrieval. Sometimes encoding and storage of memories is just fine, but retrieval is a problem. The metaphor I think of is that the book might be in the library, but the card catalog or computer search process for the book is missing or messed up. Here is what Sanjay says about retrieval:
If you struggle with remembering, say, people’s names and you’re not suffering from a physical disease or dementia, it’s usually not the failing of your entire memory system. It could be a lack of attention at the time you were being introduced and first heard the person’s name. It could also be an inefficient retrieval system. In those cases, people often feel like the name is “on the tip of their tongue.” Sometimes that can easily be rectified by sharpening your memory skills for that particular weakness, encoding or retrieval. Many memory champions started off believing they had poor memory until they spent time practicing techniques focusing on a very specific component of memory.
Memory champions especially hone their retrieval skills. A fun book on that is Moonwalking with Einstein: The Art and Science of Remembering Everything by Joshua Foer. You can get a taste of that book from my post “Joshua Foer on Memory.”
I have several other posts on learning. Take a look at these:
Conclusion. There is a lot worth knowing about memory and about learning. I am firmly convinced that even those who have been very successful in their lives academically are often operating far inside the possibility frontier for memory and learning.
Update: There is an interesting Twitter discussion between Noah and Pras Francis here.
It is good to praise and give thanks for those we have looked up to and admired. Lowell Bennion was one of those for me. I spent 8 weeks in each of the summers of 1972, 1973, 1974 and 1978 at the Teton Valley Boys’ Ranch that Lowell Bennion established, first as one of the boys and in 1978 as a counselor. The Teton Valley Boys’ Ranch did a lot to help me grow up. Though Dr. Bennion, we called him, was quite cerebral and led thoughtful discussions in the evenings, the ranch helped me balance out bookishness with a wide variety of manual labor in the weekday mornings (for which the boys were paid $2.50 for 4 hours out of the camp fees their parents had paid in the first place) with physical activities such as hiking, horseback riding, trampoline and competitive sports, and time with many new friends in the afternoons and on the weekends. (The Teton Valley Boys’ Ranch had a big enough impact on those who attended that alumni of the ranch have made sure that even a quarter century after Lowell Bennion’s death in 1996, a successor to the Teton Valley Boys’ Ranch exists.)
During the first few weeks I was at the ranch in 1972, I got sick and missed some workdays and asked Dr. Bennion what I should do. He suggested I work with him in the garden on some of the afternoons. So I got to know him well early on. He told me about his dissertation on Max Weber (the first book on Max Weber in English) and communicated wordlessly his love of gardening. He taught the principle of continuing to try to improve throughout life by apologizing for very mild profanity (“golly,” “by Jove”) and saying he was trying stop.
To the boys more generally, he said other memorable things. When we were building a barn, he talked about his hope that it would be beautiful. Combining a humanitarian lesson with an invocation of God, he said that painting widows’ fences as a way to get the favor of God was a substitute for the fire insurance he couldn’t buy for the ranch. With a largely Mormon context of trying to steer us toward avoiding premarital sex, he recommended not “going steady” with one woman until one was ready to marry.
Dr. Bennion communicated one key value by having the ranch quite literally take on at least one juvenile delinquent each summer to try to help them reform. This was costly in many ways, but he didn’t want to give up on people.
But beyond any of these specifics, it was Dr. Bennion’s presence that was most impressive. His soft-spoken, articulate wisdom was backed up by a calm centeredness. That example has provided me with a clear picture of what it looks like to be a good man. My Dad has some of that, but it was even more striking in Lowell Bennion.
I wish everyone were as lucky as I have been to have clear examples of deeply good men and deeply good women in their lives. Those of us who have been that lucky should tell stories about our heroes to bolster everyone’s faith in human potential.
Postscript: I’d love to connect with old friends from the Teton Valley Boys’ Ranch I have lost track of. Contact me on Facebook! I wish it had existed back then so we wouldn’t have fallen out of touch.
Hat tip to Joseph Kimball